NewsNEWS
Featured products
Contact Us
Centrifugal pump curve
2025-07-11Centrifugal Pump Curve: Your Essential Guide to Pump Performance
Selecting the right centrifugal pump is critical for efficient system operation. The centrifugal pump curve is the indispensable tool for this task. Understanding this graph is non-negotiable for engineers and operators. It reveals exactly how a pump performs under various conditions. Mastering the pump curve ensures optimal selection and operation.
What Exactly is a Centrifugal Pump Curve?
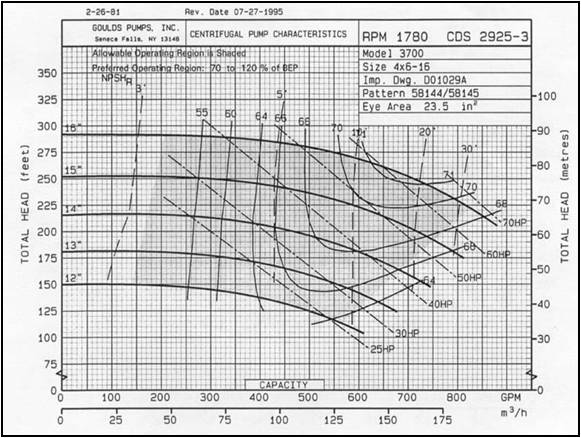
A centrifugal pump performance curve is a graphical representation. It plots the relationship between key pump operational parameters. Primarily, it shows Flow Rate (Q – usually in GPM or m³/h) on the X-axis. Head (H – usually in feet or meters of liquid) is plotted on the Y-axis. This HQ curve forms the core of the pump characteristic curve. Other parameters like efficiency, power, and NPSH Required are often overlaid.
Key Components of the Pump Performance Curve:
-
Head vs. Flow (HQ Curve): This is the fundamental line. It shows the head a pump generates at different flow rates. Typically, head decreases as flow increases. The shape of this centrifugal pump curve is unique to each pump model and speed.
-
Efficiency Curves: These islands show pump efficiency at different operating points. Peak efficiency is the sweet spot for energy savings. Operating near this point on the pump curve is ideal.
-
Brake Horsepower (BHP) Curves: This line shows the power the pump shaft requires. Power generally increases with flow. Matching motor power to the pump curve prevents overload.
-
NPSH Required Curve: This critical line shows the Net Positive Suction Head the pump needs to avoid cavitation. It increases with flow. System NPSHA must exceed this curve value.
Interpreting the Centrifugal Pump Curve:
The operating point is where the pump performance curve intersects the system resistance curve. This system curve represents the head needed to overcome friction and elevation at each flow. You must know your system curve to use the centrifugal pump curve effectively. Changing system conditions shifts this operating point.
Why is the Centrifugal Pump Curve So Important?
-
Pump Selection: It’s the primary tool for choosing the correct pump size and type for your specific flow and head requirements. Matching the pump curve to your system is essential.
-
Performance Prediction: You can accurately predict flow, head, power draw, and efficiency at any point on the HQ curve.
-
Efficiency Optimization: Identify the Best Efficiency Point (BEP) to minimize energy costs. Avoid operating far from BEP on the pump characteristic curve.
-
Avoiding Damage: Ensure operation is within the pump’s allowable operating range (AOR). Stay clear of regions causing cavitation (low NPSH) or motor overload (high flow).
-
Speed/Impeller Changes: Understand how pump speed changes (Affinity Laws) or trimming the impeller diameter will shift the entire centrifugal pump curve.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool
pump curve for selection, operation, and troubleshooting. Mastering the centrifugal pump curve is fundamental knowledge.





